Shop Products
Forward Transfection or Reverse Transfection?
Forward and reverse transfection protocols each have their significant uses in research. The main protocol difference between forward and reverse transfection is whether or not the cells are plated the day before transfection (as in forward transfection) or seeded at the same time of the transfection. Forward transfection is commonly used in situations where the cells need to be already attached and in a growth phase prior to the nucleic acid + transfection reagent complex is applied. In contrast, a reverse transfection is the process in which the nucleic acid + transfection reagent complex is assembled in the tissue culture plate and then the cells are seeded into the wells. There are many benefits to the reverse transfection method, including:
- The method is ideal for high-throughput screening since reverse transfection is compatible with automated robots
- The lack of needing to pre-plate cells saves a day
- High efficiency of the reverse transfection decreases the amount of nucleic acid used
- Unlike forward transfection, the transfection reagent can remain in contact with the cells for 24-72 hours
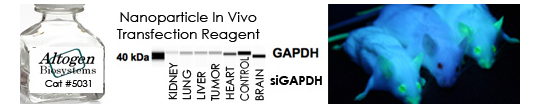
Please see full list of Altogen Biosystems transfection products here.




Sorry, comments are closed for this post.