Description
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.
Transfection Reagent for SKNAS Cells (Neuroblastoma Cells)
- Proprietary cationic lipids formulation
-
A proven reagent for establishing stable cell lines
-
Optimized transfection protocols are adapted for use with both standard & reverse transfection methods
-
Download in vitro SKNAS transfection protocol: [PDF]
- Download SKNAS CRISPR/Cas9 transfection protocol: [PDF]
- Download PowerPoint presentation for SKNAS cells transfection kit: [PPT]
- UPC/GTIN/EAN: 860002089704
-
Brand: ALTOGEN®, developed and manufactured by Altogen Biosystems
Transfection Efficiency:
Reagent exhibits at least 90% transfection efficiency of siRNA delivery. Transfection efficiency was determined by qRT-PCR.
Product Description:
Optimized transfection kit for high transfection efficiency of SKNAS cell line, a human neuroblastoma cells. Compatible with DNA and RNA transfection.
Transfection Protocol and SDS:
Download Altogen Biosystems SKNAS Transfection Protocol: [PDF]
Download SDS: [PDF]
SKNAS Cell Line:
Neuroblastoma originates from embryonic neural crest cells and is the most common extracranial solid tumor, affecting children and leading to poor prognosis due to bone metastasis. According to a 2014 article in the Journal of Bone Oncology, mice inoculated with the SK-N-AS neuroblastoma cell line developed bone metastasis like most human neuroblastoma patients. Neuroblastoma represents nearly 6% of all childhood malignancies, with approximately 700 new cases diagnosed annually in the United States, as per the American Cancer Society. The SK-N-AS cell line is isolated from a bone marrow metastasis of a 6-year old female. SK-N-AS is hyperdiploid human cell line with the modal chromosome number of 47. Normal chromosomes N9 and N22 are single. SK-N-AS are distributed for research purposes only by the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. The SK-N-SH line was derived by J.L. Biedler and is different from SK-N-MC as it displays higher levels of dopamine – beta-hydroxylase as well as a longer doubling time. Also, SK-N-SH is used in cell-mediated cytotoxicity assays as a target cell line. Frataxin-depleted cells display actin network reorganization that can be observed in fibroblasts. The cells were similar to control SK-N-AS cells after Nrf2 staining. It has been shown that treating control SKNAS cells by oligomycin or tBHQ can result in the accumulation of NADH quinone oxidoreductase, glutathione-S-transferase subunit 1 and glutathione reductase. These cells are known to produce large amounts of IGF-2 and express type 1 IGF (insulin-like growth factor) receptors. SK-N-AS cells can be useful in the study or search for medical treatments for certain types of brain cancer. Altogen Biosystems offers in vitro SK-N-AS transfection reagent for neuroblastoma cells.
SK-NAS is a human neuroblastoma cell line that was established from a metastatic site in a 10-month-old female patient with stage 4 neuroblastoma. Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that arises from the developing nerve cells in the sympathetic nervous system and is most commonly diagnosed in children. SK-NAS cells have been widely used in neuroblastoma research as a model for studying the biology of this disease. They are commonly used to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying neuroblastoma tumorigenesis, as well as to evaluate the efficacy of potential neuroblastoma therapies. SK-NAS cells are known to have a high proliferation rate and can be cultured as adherent monolayers in standard tissue culture conditions. They have been shown to express markers of sympathetic nervous system development, including tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase, which are commonly used as indicators of neuroblastoma differentiation. SK-NAS cells are commonly used in drug screening assays to identify potential anti-neuroblastoma drugs. They have been shown to be sensitive to a wide range of chemotherapeutic agents, including cisplatin, doxorubicin, and etoposide, which are commonly used in the treatment of neuroblastoma. Additionally, SK-NAS cells have been used to test the efficacy of novel immunotherapeutic approaches, such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in the treatment of neuroblastoma.
SKNAS cell line mutations:
| NRAS | 4893 | 37 | 1 | 115256530 | 115256530 | Missense_Mutation | SNP | G | T |
| TTN | 7273 | 37 | 2 | 179434772 | 179434772 | Missense_Mutation | SNP | G | A |
| INVS | 27130 | 37 | 9 | 103062934 | 103062935 | Frame_Shift_Ins | INS | – | A |
| SCAF4 | 57466 | 37 | 21 | 33044507 | 33044507 | Silent | SNP | C | T |
| CDH5 | 1003 | 37 | 16 | 66426126 | 66426126 | Missense_Mutation | SNP | G | A |
| OSR1 | 130497 | 37 | 2 | 19553372 | 19553372 | Silent | SNP | C | T |
| SCN3A | 6328 | 37 | 2 | 166012375 | 166012375 | Missense_Mutation | SNP | C | T |
| BEND4 | 389206 | 37 | 4 | 42145872 | 42145872 | Silent | SNP | G | A |
| NFATC1 | 4772 | 37 | 18 | 77171266 | 77171266 | Missense_Mutation | SNP | G | A |
| RAP1GAP | 5909 | 37 | 1 | 21934790 | 21934790 | Silent | SNP | G | A |
| ZDHHC18 | 84243 | 37 | 1 | 27159025 | 27159025 | Silent | SNP | G | A |
Data:
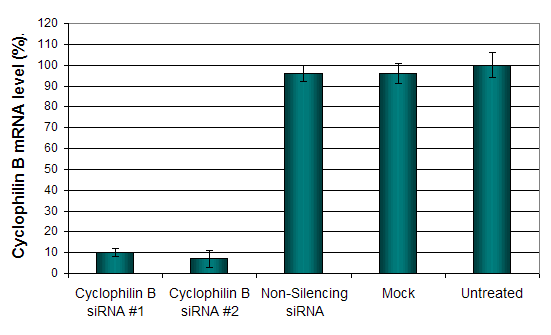
Figure 1. Cyclophilin B silencing efficiency was determined by qRT-PCR in the SKNAS cells transfected by Cyclophilin B siRNA or non-silencing siRNA control following the recommended transfection protocol. Cyclophilin mRNA expression levels were measured 48 hours post-transfection. 18S rRNA levels were used to normalize the Cyclophilin B data. Values are normalized to untreated sample. Data are presented as means ± SD (n=3).

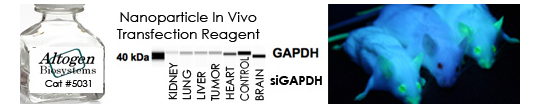
Figure 2. Protein expression of Cyclophilin B in SKNAS cells. DNA plasmid expressing Cyclophilin B or siRNA targeting Cyclophilin B were transfected into SKNAS cells following Altogen Biosystems transfection protocol. At 72 hours post-transfection the cells were analyzed by Western Blot for protein expression levels (normalized by total protein, 10 µg of total protein loaded per each well). Untreated cells used as a negative control.
Selected SK-N-AS transfection reagent citation references:
- Nat Commun. 2016 ;7:12057. Signal transduction controls heterogeneous NF-κB dynamics and target gene expression through cytokine-specific refractory states. Adamson A et al [PDF]
- Endocrine-Related Cancer 2016. 23(8):595-607. Role of protein S in castration-resistant prostate cancer-like cells. Ning et al [PDF]
- RNA. 2010 16(11):2108-19. RNase L releases a small RNA from HCV RNA that refolds … Malathi et al [PDF]
Altogen Biosystems manufacturers over 100 pre-optimized in vitro transfection kits for cancer cell lines and primary cells, elecroporation products, and tissue-targeted in vivo delivery reagents for life science research. Advanced formulation of reagents and optimized transfection protocols provide efficient intracellular delivery of protein, DNA, mRNA, shRNA and siRNA molecules. Read more about transfection technology at Altogen’s Transfection Resource. Altogen Labs provides safety and efficacy preclinical research services. GLP-compliant studies for IND applications, and drug development, including over 90 in-house validated xenograft models, safety toxicology, etc (visit AltogenLabs.com).
Volume Options:
- 0.5 ml (Catalog #3259)
- 1.5 ml (Catalog #3260)
- 1.5 ml CRISPR (Catalog #2194)
- 8.0 ml (Catalog #7012)
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.