Shop Products
What is Oncogene
cancer. Oncogenes can be activated or overexpressed in cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth, tumor formation, and metastasis.
Oncogenes are normal genes that encode for proteins involved in regulating cell growth and division. However, mutations or abnormalities in these genes can lead to their activation or overexpression, which can result in the abnormal regulation of cell growth and division, leading to the development of cancer.
There are several types of oncogenes, including proto-oncogenes, which are normal genes that can become oncogenes due to mutations or overexpression, and viral oncogenes, which are derived from viruses that can integrate into the host cell’s genome and activate oncogenic pathways.
Oncogenes play a crucial role in the development and progression of cancer, and their identification and targeting have led to the development of targeted cancer therapies, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies.
Some examples of oncogenes include the RAS family of oncogenes, which are commonly mutated in various types of cancer, and the HER2 oncogene, which is overexpressed in certain types of breast and gastric cancers.

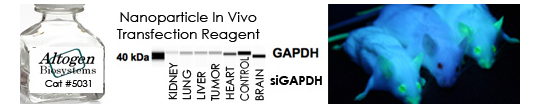



Sorry, comments are closed for this post.