Shop Products
What is Transfection Reagent
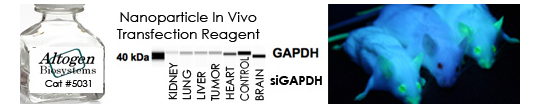
A transfection reagent is a chemical compound used to deliver genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, into cells. Transfection is the process of introducing exogenous nucleic acids into cells, which can allow researchers to study gene function, gene regulation, and protein expression in various cell types.
Transfection reagents facilitate the delivery of genetic material by forming complexes with the nucleic acid molecules and promoting their uptake by cells. These complexes typically consist of the nucleic acid molecule, the transfection reagent, and any additional components that may be necessary for efficient transfection, such as serum or growth factors.
There are various types of transfection reagents available, including cationic lipids, cationic polymers, and other synthetic or natural molecules that can interact with the cell membrane and facilitate the uptake of nucleic acids into cells. Some transfection reagents can be specific for certain types of cells or certain types of nucleic acids, and the choice of the transfection reagent will depend on the specific experimental needs and cell types.
Transfection reagents are widely used in molecular biology and biotechnology research, as well as in the development of gene therapy and other medical applications.




Sorry, comments are closed for this post.