Description
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.
Transfection Reagent for Astrocytes (Primary Astrocyte Cells, Astroglia)
-
Proprietary cationic lipids formulation
-
High transfection efficiency of small RNA (siRNA, shRNA, miRNA), mRNA, pDNA
-
Effective and robust intracellular delivery
-
Kit includes Transfection Enhancer reagent
-
Produces consistent results, lot-to-lot, plate-to-plate, and well-to-well
-
Work in the presence of serum
-
A proven reagent for establishing stable cell lines
-
Optimized transfection protocols are adapted for use with both standard & reverse transfection methods
-
Download in vitro Astrocyte transfection protocol: [PDF]
- Download Astrocyte CRISPR/Cas9 transfection protocol: [PDF]
-
Download PowerPoint presentation for Astrocyte cells transfection kit: [PPT]
- UPC/GTIN/EAN: 860002089729
-
Brand: ALTOGEN®, developed and manufactured by Altogen Biosystems
Transfection Efficiency:
Reagent exhibits at least 70% transfection efficiency of siRNA delivery. Transfection efficiency was determined by qRT-PCR.
Transfection Protocol and SDS:
Download Altogen Biosystems Astrocyte Transfection Protocol: [PDF]
Download SDS: [PDF]
Product Description:
Optimized transfection kit for high transfection efficiency of astrocyte cells . Used in molecular biology research applications to facilitate the introduction of foreign nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) into cultured astrocyte cells.
Astrocyte Cells (Primary Astrocytes and Astroglia):
The human brain comprises two major cell types: neurons and glia. Neurons are responsible for transmitting nerve signals while glia safeguard neurons. Astrocytes, a sort of glial cells, make over 50% of all brain cells. In the event of any distress to the Central Nervous System (CNS), a process called gliosis is triggered. Gliosis involves the rapid differentiation of glial cells to provide mechanical support to neurons. However, excessive gliosis is symptomatic of various forms of brain cancer. Per the study published in the January 2016 issue of Tumor Biology, astrocytes play an important role in controlling the environment around a tumor. Astrocytes retard the detection of cancer cells by the immune system and help enhance their proliferation. Preclinical research targeting astrocytes can provide valuable insight into molecular pathways that can curb tumors. Transfection is a well-regarded technique to conduct preclinical research in many different cells, including astrocytes. Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. Astrocytes are supportive cells, and their functions include biochemical support of endothelial cells, which form the blood-brain barrier, providing nutrients to the nerve tissue, extracellular K+ level regulation, neurotransmitters removal, and helping repair the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries. They are also dependent on myelination and synapses formation. Many primary astrocytes express the intermediate filament glial fibrillary acidic protein or GFAP. Research indicates that astrocytes communicate with neurons through the release of gliotransmitters via a calcium ion process. There are three types of astrocytes in the central nervous system: fibrous, protoplasmic and radial. It is believed astrocytes cell bodies are separate and do not overlap.
Astrocytes, also known as astroglia, are cells in living organisms that make up parts of the nervous system, particularly in the brain and spinal cord. They work with the body’s natural response to trauma in the brain and spinal cord, by repairing and providing nutrients to affected areas. Because of this, astrocytes may be useful in the study of specific medical treatments for patients suffering from spinal cord injuries. These cells are crucial to research in the field of neuroscience. Astrocytes are a type of glial cell in the central nervous system (CNS) that provide support and protection for neurons. These cells are involved in a variety of functions, including regulating the extracellular environment of the brain, providing structural support for neurons, and modulating synaptic transmission. Astrocyte cells are commonly cultured as adherent monolayers and have been shown to express markers of astrocytic differentiation, such as glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). They are also known to be responsive to certain signaling molecules, such as glutamate and ATP, which are involved in regulating synaptic transmission. In addition to their use in studying neurological diseases, astrocyte cells have been used to study the effects of potential therapeutic agents for CNS disorders. Primary cell cultures are used in biological and gene therapy studies and serve as valuable model systems that may more accurately represent the biology of healthy cells. Many cultured cell lines, as well as the majority of primary cell cultures, can be transfected with exogenous nucleic acids when appropriate transfection approaches are employed. Since the majority of transfection methods causes significant toxicity in primary cell cultures, optimizing this procedure, specifically the protocol and reagents to be utilized, is essential for developing an effective transfection strategies for a given cell type. ALTOGEN® Kits for primary cells and sensitive cell lines have been designed to have significantly lower cytotoxicity than other alternatives.
Data:
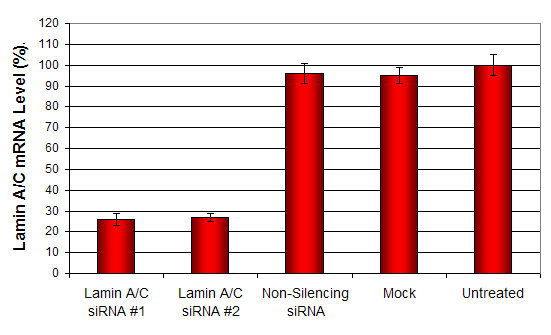
Figure 1. SiRNAs targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA were transfected into actrocyte cells following the recommended protocol. At 48 hours post-transfection the cells were analyzed by qRT-PCR for gene expression levels. 18S rRNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Values are normalized to untreated sample. Data are means ± SD (n=3).
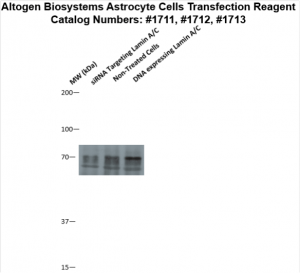
Figure 2. Protein expression of Lamin A/C in Astrocyte cells. DNA plasmid expressing Lamin A/C or siRNA targeting Lamin A/C were transfected into Astrocyte cells following Altogen Biosystems transfection protocol. At 72 hours post-transfection the cells were analyzed by Western Blot for protein expression levels (normalized by total protein, 10 µg of total protein loaded per each well). Untreated cells used as a negative control.
Selected Astrocyte Transfection Reagent product citations:
- Journal of Neuroscience. 2013 33(44). Foxo3a Transcriptionally Upregulates AQP4 and Induces … Kapoor et al [PDF]
- Mol Cell Biol. 2013 33(7). SCO2 induces p53-mediated apoptosis by Thr845 phosphorylation … Madan et al [PDF]
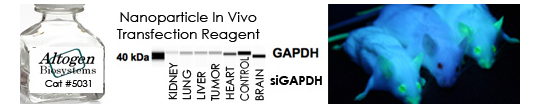
Altogen Biosystems provides pre-optimized transfection kits and electroporation products for life sciences and cancer research. Transfection protocols are optimized for individual cancer cell lines. Altogen Biosystems developed two types of in vivo delivery kits (animal transfection): 1) Tissue-targeted reagents (delivery of proteins, DNA, and RNA into liver, pancreas, or kidney tissues), and 2) Broad range in vivo biodistribution reagents (PEG-Liposome based reagent, Nanoparticle-based in vivo reagent, Lipid-based transfection kit, and Polymer-based kit). Advanced formulation of reagents and optimized transfection protocols provide efficient intracellular delivery of proteins, DNA, mRNA, shRNA, siRNA, and other negatively charged biomolecules in vitro and in vivo. Read more about transfection technology at Altogen’s Transfection Resource. Altogen Labs provides GLP compliant contract research studies for preclinical research, IND applications, and drug development. Biology CRO services include: Over 90 in-house validated xenograft models, development of stable cell lines, ELISA assay development, cell-based and tissue targeted RNAi studies, safety pharm/tox assays, and other studies (visit AltogenLabs.com).
Volume Options:
- 0.5 ml (Catalog #1711)
- 1.5 ml (Catalog #1712)
- 1.5 ml CRISPR (Catalog #2110)
- 8.0 ml (Catalog #1713)
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.