Description
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.
POLYMER-based In Vivo Transfection Kit
siRNA and plasmid DNA in vivo delivery reagent (mice and rats)
Product Description:
Biodegradable polymer-based in vivo transfection reagent, designed for efficient delivery of siRNA and plasmid DNA to multiple organs, including the lung, liver, kidney, and spleen, with minimal inflammatory response. This versatile reagent is functionally tested in mice and rats, ensuring reliable protein(s) or plasmid DNA/siRNA co-injection and direct subcutaneous tumor injection across various tumor types. Polymer-based in vivo transfection uses synthetic polymers to deliver nucleic acids like DNA or RNA into tissues, offering a safer and more versatile alternative to viral methods. Polyethyleneimine (PEI) is commonly used but can be toxic and induce inflammation, leading to the investigation of other polymers such as PLGA and PBAEs.
Altogen’s POLYMER In Vivo Transfection Reagent
- Biodegradable polymer-based in vivo transfection reagent
- No detectable inflammatory response
- Efficient delivery to the lung, liver, kidney, and spleen via systemic administration
- Efficient siRNA and plasmid DNA delivery via direct subcutaneous tumor injection (multiple tumor types)
- Functionally tested in mice and rats
- Applicable for plasmid DNA/siRNA co-injection
- Download POLYMER-based in vivo transfection protocol: [PDF] [Word]
- Download PowerPoint presentation for POLYMER-based in vivo transfection kit: [PPT]
- Download safety data sheet: [PDF]
- UPC/GTIN/EAN: 860002089706
-
Brand: ALTOGEN®, developed and manufactured by Altogen Biosystems
Modes of administration:
- Systemic intravenous (i.v.) injection
- Direct intratumoral (i.t.) injection
DATA
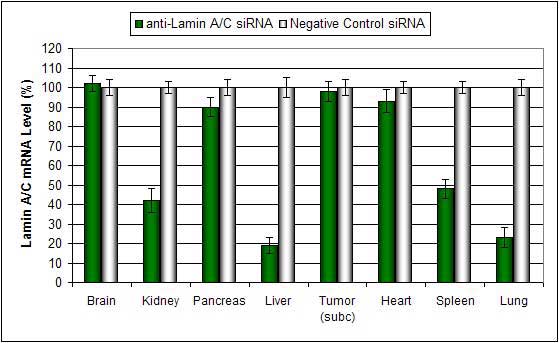
Figure 1. Systemic administration (i.v.) of Polymer-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
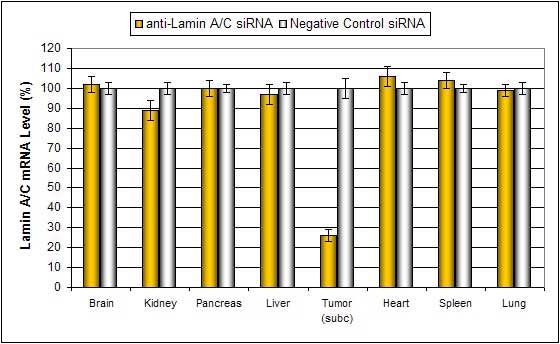
Figure 2. Intratumoral administration (i.t.) of Polymer-based In Vivo reagent conjugated with siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues were collected and RNA isolated 48 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for Lamin A/C gene expression levels. Ribosomal RNA levels were used to normalize the Lamin A/C data. Data are means ± SD (n=6).
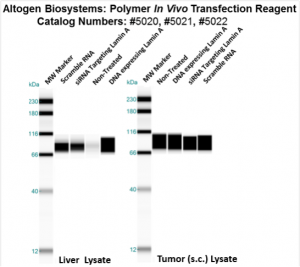
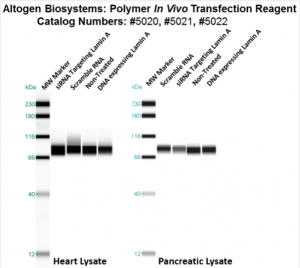
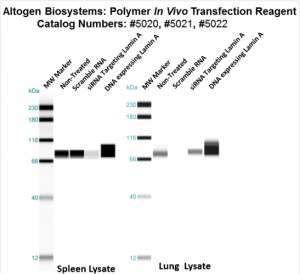
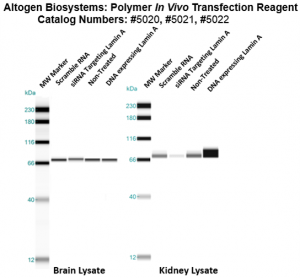
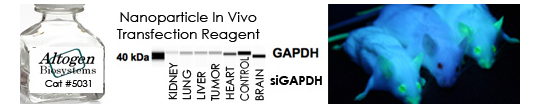
Figure 3. Systemic administration (i.v.) of Polymer In Vivo Transfection Reagent conjugated with 80 ug of chemically modified siRNA targeting Lamin A/C mRNA or non-silencing control siRNA following the recommended protocol. Tissues (Liver, Brain, Muscle, Kidney, Tumor, Heart, Spleen, Lung) were collected and total protein fraction isolated 72 hours after first injection. Samples were analyzed by Western Blot Analysis for Lamin A/C gene expression levels.
Polymer-based in vivo transfection
Polymer-based approaches for in vivo transfection involve using synthetic polymers to deliver nucleic acids, such as plasmid DNA or RNA, into tissues. This approach is a promising alternative to viral-based methods, which can have safety concerns and limited cargo capacity. One commonly used polymer for in vivo transfection is polyethyleneimine (PEI), which is cationic and can form complexes with negatively charged nucleic acids. These complexes can then be taken up by cells, allowing for expression of the encoded genes. However, PEI can be toxic and induce inflammation, so other polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) and poly(beta-amino esters) (PBAEs) have been investigated as well. Polymer-based transfection methods have been used in a variety of applications, such as gene therapy, vaccination, and tissue engineering. However, challenges remain in terms of achieving efficient and targeted delivery to specific cell types, minimizing toxicity, and achieving long-term gene expression. Ongoing research in this field is focused on developing more advanced polymer-based delivery systems that can overcome these challenges and improve the efficacy and safety of in vivo transfection.
Selected in vivo transfection product citations (ALTOGEN® IN VIVO Transfection Kits used in the following publications):
- Nature. 2008 454(7203):523-7. Innate immunity induced by composition-dependent RIG-I …Saito et al [PDF]
- Am J Pathology. 2010 177(4):1870-80. Role of ocular complement factor H in a murine model … Lyzogubov et al [PDF]
- Nature Biotechnology. 2011 29(4):341-5. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by … Alvarez-Erviti et al [PDF]
- Cancer Research. 2011 71(15):5144-53. Inhibition of miR-193a expression by… Iliopoulos et al [PDF]
- RNA. 2010 16(11):2108-19. RNase L releases a small RNA from HCV RNA that refolds … Malathi et al [PDF]
- Diabetologia. 2012 55(7):2069-79. The p47phox- and NADPH oxidase organiser 1 … Youn et al [PDF]
- British Journal of Cancer. 2012 107(3):516-26. TIGAR induces p53-mediated cell-cycle … Madan et al [PDF]
- Hypertension. 2014 63(2):353-61. Tissue transglutaminase contributes to … Liu et al [PDF]
- Circulation Research. 2010 15;107(8). Kruppel-like factor-4 transcriptionally regulates … Cowan et al [PDF]
- Hypertension. 2012 59(1):158-66. Role of uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase … Gao et al [PDF]
- Jounal of Biological Chemistry. 2012 287(4):2907. Chaperoning of mutant p53 protein … Gogna et al [PDF]
- PLoS Pathogens. 2012 8(8) Uridine composition of the poly-U/UC tract of HCV RNA … Schnell et al [PDF]
- J Proteome Res. 2012(11) Retinal proteome analysis in a mouse model of oxygen-induced … Kim et al [PDF]
- J Transl Med. 2010 15;8:133. Prevention of hyperglycemia-induced myocardial apoptosis … Zhang et al [PDF]
- Mol Cell Biol. 2013 33(7). SCO2 induces p53-mediated apoptosis by Thr845 phosphorylation … Madan et al [PDF]
- Hypertension. 2015 65(2):430-9. Neurokinin 3 receptor and phosphocholine transferase… Parchim et al [PDF]
- Gastroenterology. 2011 141(2) Differential type I interferon-mediated autophagic trafficking … Desai et al [PDF]
- PLoS Pathog. 2014 10(10) Exosomes from hepatitis C infected patients transmit HCV … Bukong et al [PDF]
Altogen’s polymer-based in vivo transfection reagent is a biodegradable polymer-based solution for efficient delivery of siRNA and plasmid DNA to organs like the lung, liver, kidney, and spleen with minimal inflammatory response. Functionally tested in mice and rats, this reagent ensures reliable co-injection and direct subcutaneous tumor injection across multiple tumor types. We also provide biology contract research services using these reagents. Altogen Labs provides GLP-compliant contract research studies for pre-clinical research, IND applications, and drug development. Biology CRO services includes: Xenograft models (over 90), development of stable cell lines, ELISA assay development, cell-based and tissue targeted RNAi studies, safety pharm/tox assays, and many other IND-enabling contract research studies (visit AltogenLabs.com).
Volume Options:
- 0.5 ml – 10 injections (Catalog #5020)
- 1.5 ml – 30 injections (Catalog #5021)
- 8.0 ml – 160 injections (Catalog #5022)
- 25 ml – 50 rat injections or 500 mouse injections (Catalog #5023)
Purchase Orders: Click “Add to Cart” button to order, then email PO to orders@altogen.com.
Product Availability: In Stock.